1. Text functions
Text functions can perform various treatments on strings of characters. For example :
- Change the case of a string, i.e. convert it to upper or lower case
- Extract a part of a string of characters
- Search for a string within a string
- Replace text in a string with another text
- etc...
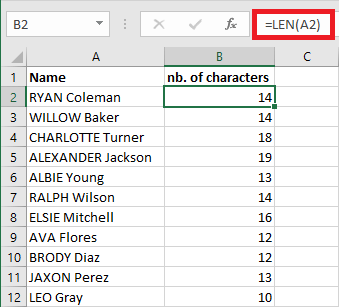
Fonction LEN
The LEN function returns the number of characters in a string.
Syntax
LEN(text)
Arguments
text: the string we want to have its number of characters
Result
The number of characters of the string given as argument
Example
The formula written in B2 is : "=LEN(A2)"
UPPER, LOWER and PROPER functions
The UPPER, LOWER and PROPER functions change the case of a string of characters:
- The UPPER function converts a string of characters to upper case
- The LOWER function converts a string of characters to lower case
- The PROPER function puts the first letter of each word of a string in upper case and the rest of the word in lower case
Syntax
UPPER(text)
LOWER(text)
PROPER(text)
Arguments
text : the character string to be converted
Résult
The string after conversion
Example
The formula written in B2 is : "=UPPER(A2)"
The formula written in C2 is : "=LOWER(A2)"
The formula written in D2 is : "=PROPER(A2)"

MID Function
The MID function returns a part of a string.
Syntax
MID(text;start_num;num_char)
Arguments
text : the string from which a part will be extracted
start_num : number of the starting character of the extraction
num_char : number of characters to be extracted from the start_num position
Result
The string extracted from the one given as an argument having num_char characters from the start_num poisition
Example
The formula written in B2 is : "=MID(A2,5,10)"
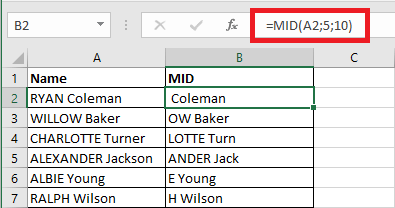
Note that when there are not enough characters left than specified in the third argument, then Excel returns the remaining characters and does not return an error. This is the case for example in cell B2 where 8 characters are returned instead of 10.
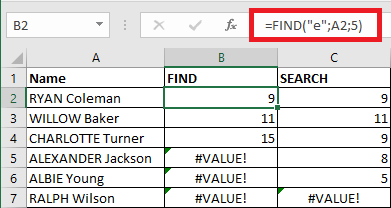
FIND and SEARCH functions
The functions FIND and SEARCH search for a character or string of characters in another string and return the position of the first occurrence found. These functions return the error #VALUE! if they do not find.
The difference between these two functions is that FIND is case sensitive, but SEARCH is not. This means that for SEARCH "e" and "E", for example, it is the same thing. Another difference is that with the SEARCH function, it is possible to use the wildcards "?" and "*" in the search text.
Syntax
TROUVE(find_text;within_text;start_num)
SEARCH(find_text;within_text;start_num)
Arguments
find_text : the character or string you wish to search for
within_text : the string where find_text will be searched
start_num : position in within_text where the search will start. This means that characters before this position will be ignored in the search. This argument is optional. If it is ignored, the search will start at position 1.
Result
The position where find_text is found in within_text. Or the error #VALUE! if the searched text is not found.
Example
The formula written in B2 is : "=FIND("e",A2,1)"
The formula written in C2 is : "=SEARCH("e",A2,1)"
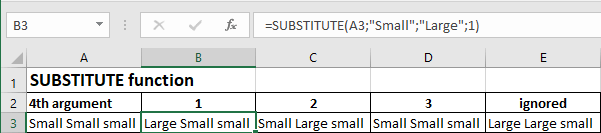
SUBSTITUTE function
The SUBSTITUTE function replaces characters with other characters in a text.
Syntax
SUBSTITUTE(text; old_text; new_text; instance_num)
Arguments
text : the string where the replacement will take place
od_text : the text that will be searched to be replaced
new_text : the text that will replace old_text in the first argument text
instance_num : number of the occurrence of old_text that will be replaced. If it is ignored, then all occurrences of old_text will be replaced by new_text.
Result
The text obtained after the replacement
Example
The formula written in B2 is : "=SUBSTITUTE(A3,"Small","Large",1)" : the first occurrence is replaced
The formula written in C2 is : "=SUBSTITUTE(A3,"Small","Large",2)" : the second occurrence is replaced
The formula written in D2 is : "=SUBSTITUTE(A3,"Small","Large",3)" : nothing is replaced because there is no third occurrence
The formula written in E2 is : "=SUBSTITUTE(A3,"Small","Large")" : all occurrences are replaced, as the fourth argument is ignored
NB. Note that the SUBSTITUTE function is case sensitive; "small" is not considered an occurrence of "Small".